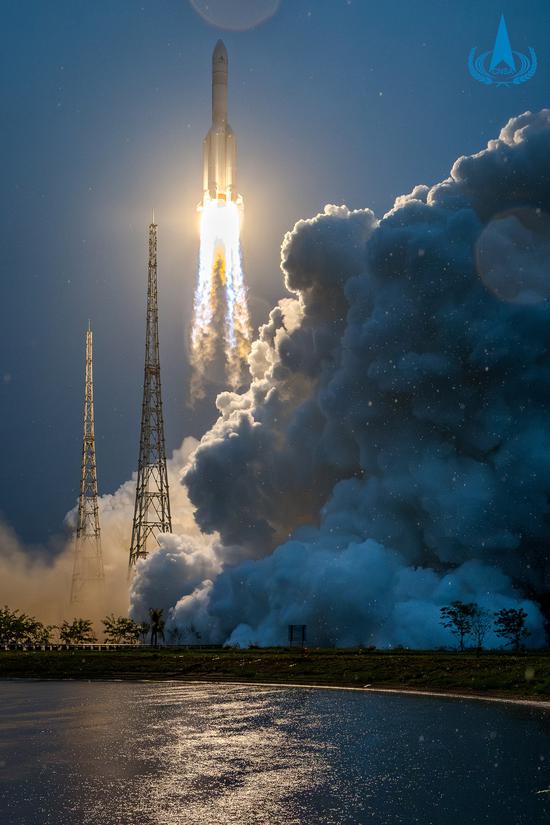

A Long March 5 heavy-lift rocket, carrying the Chang'e 6 robotic lunar probe, blasts off on Friday from the Wenchang Space Launch Center in Hainan province. (Photo/China National Space Administration)
Scientific benefits
The lunar far side is the hemisphere of the moon permanently facing away from Earth due to tidal forces on the planet. As it is never visible from Earth, that region was once dubbed the "dark side of the moon" even though it receives just as much sunlight as the near side.
The moon's far side has been extensively photographed by various spacecraft, starting with a Soviet probe in 1959. However, no probe had touched down on its surface until China's Chang'e 4 mission, which landed in the South Pole-Aitken Basin in January 2019.
Due to its many mysteries, the far side has been a subject of scientific speculation and popular sci-fi culture since the Apollo era.
As the landing destination, the South Pole-Aitken Basin is believed to hold clues to intriguing and important science questions.
There has been a popular hypothesis that the basin was formed through the impact of a massive asteroid, around 200 kilometers in diameter. The collision was so powerful that it excavated some of the lunar mantle — mate-rial between the lunar core and the crust — and brought it to the surface. The physical characteristics of the gigantic crater thus appear to be different from other lunar regions.
Chinese researchers have found that the layer of soil on the far side is much thicker than on the near side, but they have yet to find out why the crust on the two sides drastically differs in terms of thickness.
Scientists around the world called for a sample-return mission to the far side, underlining that the advantage of going there is the potential of learning more about the interior composition of the moon.
According to mission planners at the China National Space Administration, many scientists at home and abroad have said they are eagerly waiting for the Chang'e 6 probe to bring back samples from the far side, because such materials will hold high scientific value.
For instance, samples brought back by the Chang'e 5 probe have helped scientists find that there were volcanic activities on the moon's near side around 2 billion years ago. Samples from the far side will allow them to verify the hypothesis that volcanoes became inactive on that hemisphere about 4 billion years ago.
Professor Martin Sweeting, a fellow of the Royal Society of the United Kingdom and a distinguished professor of space engineering at the University of Surrey, told China Daily before Friday's launch that he was "looking forward to the launch of Chang'e 6 that will, for the very first time, bring unique samples from the far side of the moon".
Sweeting said that landing and retrieving samples on the far side, out of the Earth's direct sight and communication, is a "very complex and demanding engineering activity" that will rely on advanced control systems and robotics on the surface and communications via the Queqiao 2 relay satellite in lunar orbit.
"The surface on the far side is very different to the near side ... with a multitude of impact craters and relatively few flat and dark areas, so comparing the composition of the far side samples from Chang'e 6 with those previously gathered from the near side will be of great scientific value to the international community," he said.
Giuseppe Reibaldi, president and founder of the Moon Village Association, a Vienna-based NGO, and executive secretary of the Global Expert Group on Sustainable Lunar Activities, said the Chang'e 6 mission will combine the challenges of the previous two Chinese lunar expeditions — the Chang'e 4 probe that made the first landing on the far side and the Chang'e 5 that recovered samples from the moon's near side.
The lunar formation and composition are not well understood till today, and analyzing the samples from the far side will make a major contribution toward understanding them, said Reibaldi, who worked for the European Space Agency for 35 years.
"It is expected that some materials recovered from the far side will be made available to the international science community, to give more scientists access to these samples, like it was done in case of Chang'e 4," he added.
International cooperation
In addition to the unprecedented attempt to collect samples from the lunar far side, the Chang'e 6 probe also holds significance because it is expected to bring three European science payloads to the far side.
According to the space administration, there is a radon measuring instrument from France's national space agency on the Chang'e 6 lander, which will help study the movement of lunar dust and some volatile chemicals between the lunar regolith, a layer of unconsolidated rocky material, and the lunar exosphere.
The second payload is a passive laser retroreflector from Italy's National Institute for Nuclear Physics, which will be used as a laser range-finder for the Chang'e 6 lander.
The third payload, developed by the Swedish Institute of Space Physics with support from the European Space Agency, will be the first-ever dedicated negative ion instrument flown beyond Earth. It will seek to detect negative ions emitted from the lunar surface as a result of interaction with solar winds.
More than 20 proposals from foreign space agencies and research organizations contested for the golden opportunity to join the Chang'e 6 mission to reach the far side. The three from Europe emerged as winners.
This is not the first time for China to offer opportunities to foreign scientists to deploy their science equipment on the moon. During the Chang'e 4 mission, the Chinese probe had carried German and Swedish sensing devices to the far side.













































 京公網安備 11010202009201號
京公網安備 11010202009201號